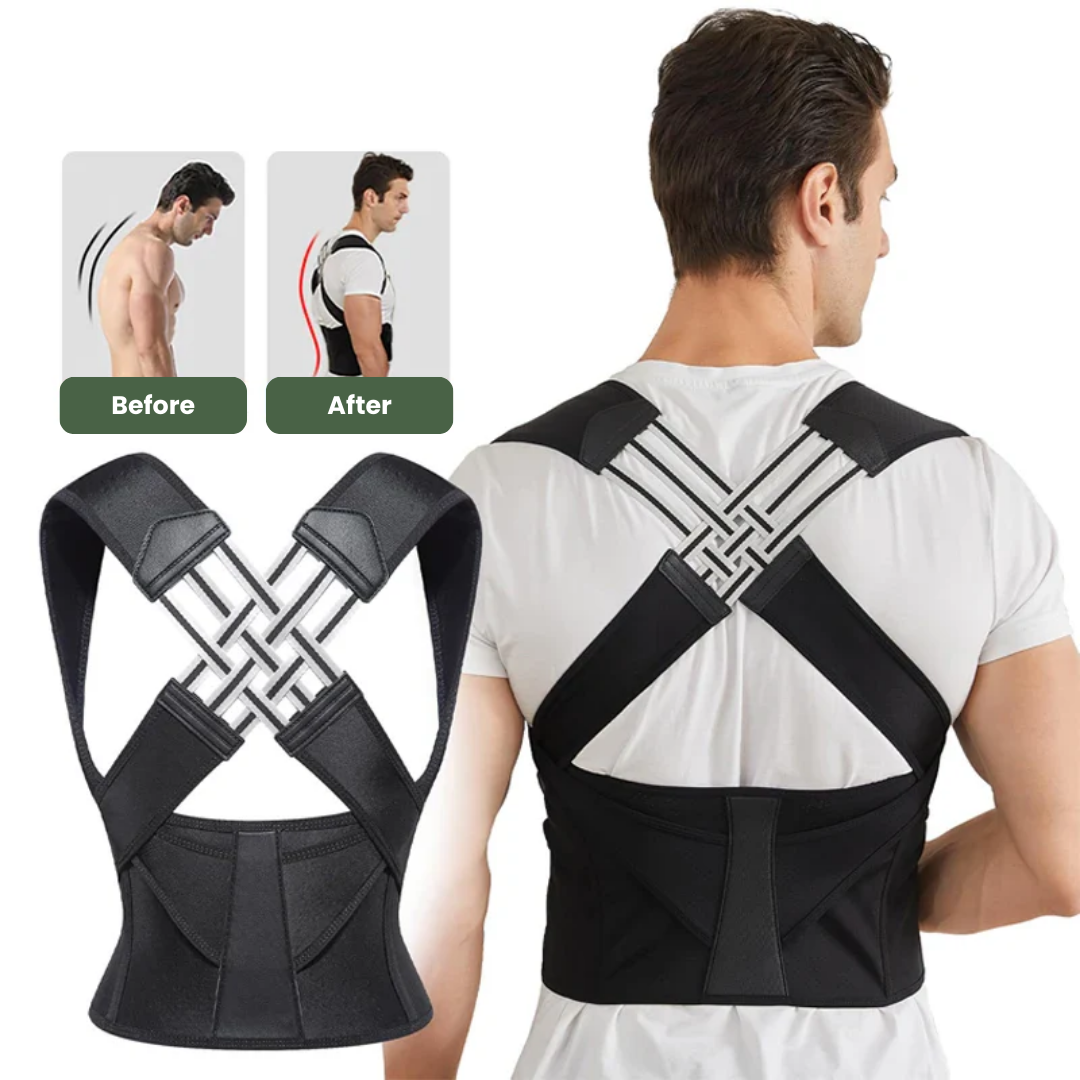
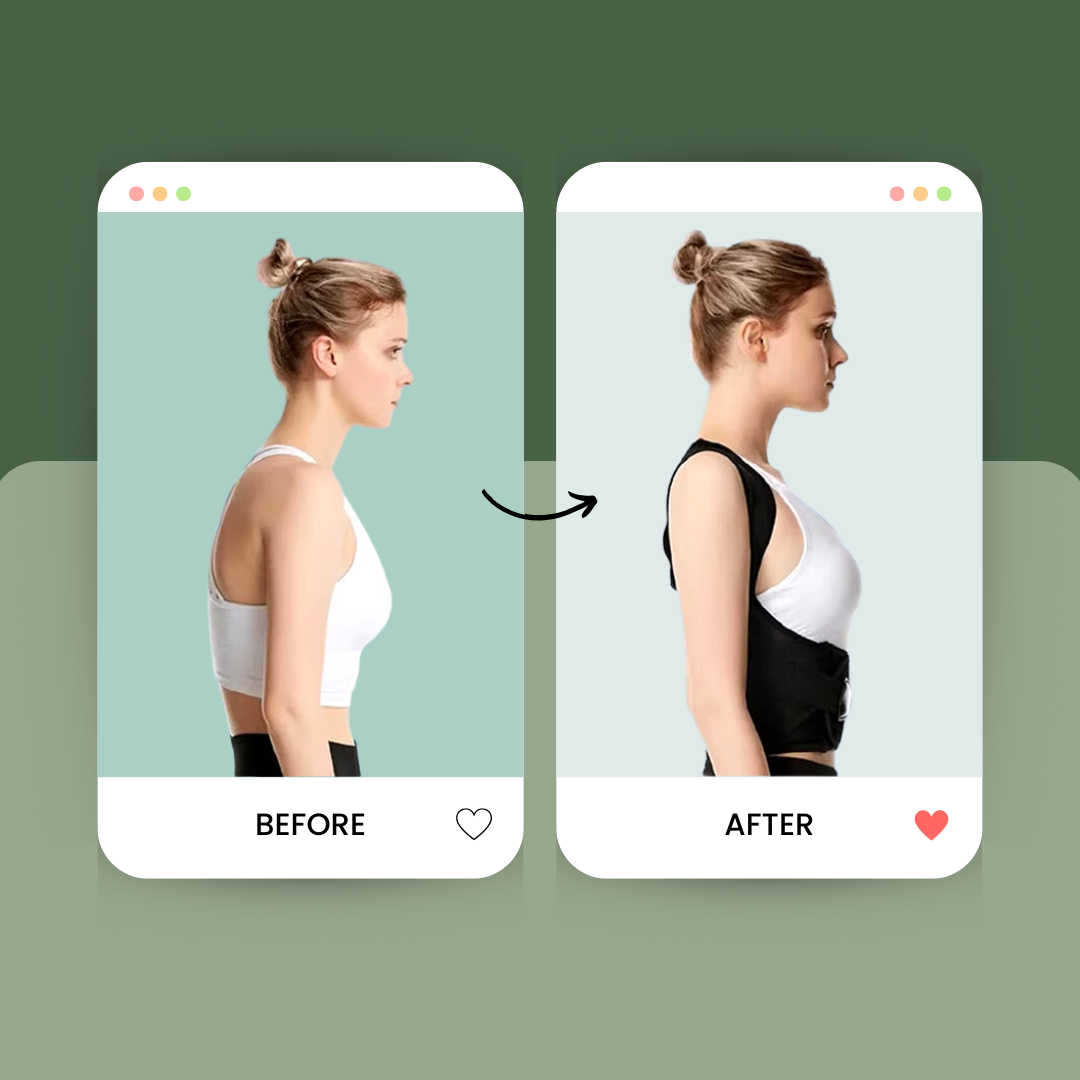
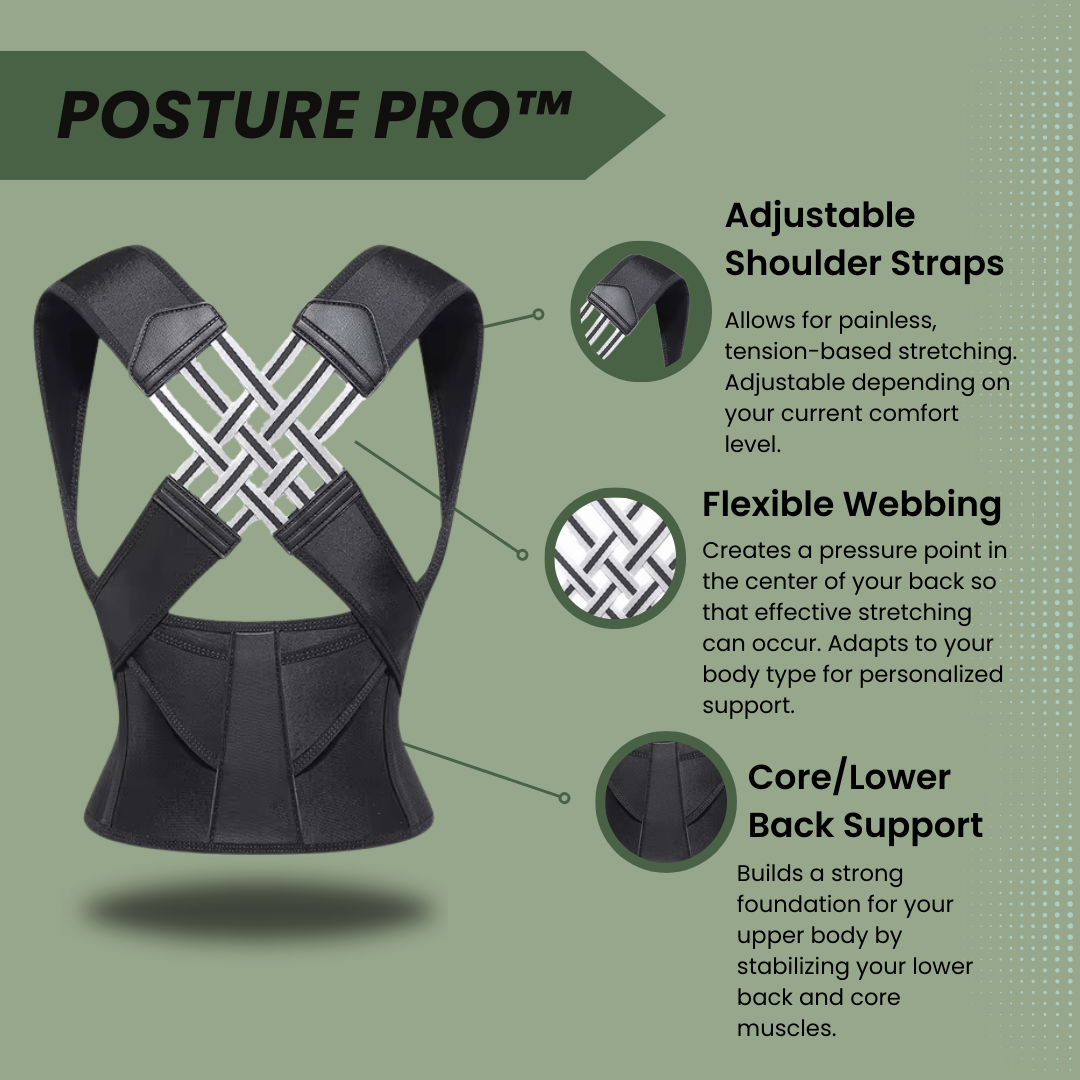
Many people struggle with bad posture without realizing its impact. Posture, including types of posture (static vs. dynamic), affects your health greatly. This blog will guide you through understanding and improving both static and dynamic posture.
Keep reading to learn more!
Key Takeaways
- Posture affects health greatly, with static posture relating to how one holds the body when not moving and dynamic posture involving movement such as walking. Good posture supports proper body alignment and reduces strain on muscles.
- Poor postures like forward head posture, sway back posture, and flat back posture can lead to musculoskeletal issues over time including pain, discomfort, and decreased mobility. Recognizing these types is key to improving overall health.
- Simple exercises like Wall Angels, planks, chest opener stretches alongside ergonomic support from furniture can significantly improve both static and dynamic postures. Regular practice helps maintain good alignment.
- Consulting professionals for personalized advice on correct body positioning can offer tailored strategies for enhancing stability and preventing common postural problems.
- Awareness of how one's environment impacts posture is important; ergonomic adjustments in workspaces encourage healthy sitting positions which benefit long-term wellness.
Understanding Posture
Posture refers to the way we hold our bodies during different activities. It plays a crucial role in our overall health and can impact everything from comfort to musculoskeletal function.
What is posture?
Posture defines how joints align under the force of gravity. It reflects body position, whether standing, sitting, or lying down. Static posture involves maintaining a stable position without movement.
This type is crucial for resting and can influence overall health and well-being.
Dynamic posture occurs during movement, like walking or running. It shows how we hold ourselves while in action. Good posture promotes proper alignment of the musculoskeletal system.
By understanding both static and dynamic postures, individuals can improve their personal posture and reduce risks associated with bad habits.
Good posture is essential for overall health and wellbeing.
How does posture affect health?
Good posture plays a significant role in overall health and wellbeing. It supports proper body alignment and reduces strain on muscles and joints. Static posture refers to how you hold your body when not moving, such as standing or sitting.
Maintaining good static posture can prevent discomfort and promote spinal health. Dynamic posture involves your body's position while moving, like walking or engaging in physical activities.
Proper dynamic posture allows for efficient movement patterns, reducing the risk of injury.
Bad posture can lead to various musculoskeletal issues over time. Forward head posture often results from poor habits like slouching while using devices. This condition may cause neck pain and headaches due to muscle strain.
Sway back posture can develop from a lack of core stability, leading to lower back pain and discomfort during daily tasks. Flat back posture may limit mobility and increase stress on the spine, affecting overall function.
Understanding these types helps improve body alignment for better health outcomes.
Types of Posture
Posture plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It influences how we move and how our bodies feel during various activities.
Static Posture

Static posture refers to how your body holds itself while standing, sitting, lying down, or kneeling. It requires you to maintain a stable position without any movement. This type of posture plays a significant role in your overall health and wellbeing.
Understanding static posture helps in recognizing correct body alignment relative to gravity. Good static posture supports your joints and reduces strain on muscles. Poor static posture can lead to discomfort and long-term health issues.
Focusing on improving this aspect can enhance health and prevent musculoskeletal problems over time.
Dynamic Posture
Dynamic posture refers to how you hold your body while moving. This type of posture is crucial during activities like walking, running, or playing sports. Good dynamic posture helps you stay balanced and active.
It allows the muscles to work properly while keeping your joints aligned.
Maintaining proper alignment in dynamic posture can prevent injuries. Poor dynamic posture may lead to pain in the back and neck. Understanding this aspect of body posture can improve health and well-being.
Practicing mobility training also supports good movement habits and enhances overall performance in everyday tasks and physical activities.
Neutral Posture
Neutral posture represents the optimal body alignment. In this position, your joints align well under the force of gravity. You maintain a balanced posture while standing or sitting comfortably.
This state reduces strain on muscles and ligaments.
Good neutral posture supports overall health and wellbeing. It helps prevent common issues like back pain and joint discomfort. Both static posture, like sitting in a chair, and dynamic posture, such as walking, benefit from this alignment.
Adopting good postural habits improves both types of movement and can enhance physical performance over time.
Forward Head Posture
Forward Head Posture occurs when the head moves ahead of the shoulders. This misalignment can strain neck and back muscles. It often results from prolonged periods of looking down at phones or computers.
Forward Head Posture affects overall health by increasing tension in the spine and leading to headaches.
This posture is a type of static posture, as it reflects how your body holds itself while not moving. Poor alignment can also impact breathing and digestion over time. Correcting this posture involves exercises that strengthen the neck and upper back muscles.
Maintaining good ergonomics while sitting helps optimize posture throughout daily activities.
Sway Back Posture
Sway Back Posture occurs when the pelvis shifts forward and the upper body leans back. This posture often results in an exaggerated curve in the lower back. Static posture plays a crucial role here, as it reflects how your body aligns while standing or sitting still.
People with Sway Back Posture may experience several health issues. Muscle fatigue, discomfort, and potential injury can arise from this misalignment. Maintaining correct posture is vital for overall health and wellbeing.
It helps reduce risks associated with poor static postures like Sway Back Posture and supports better movement patterns during dynamic activities.
Flat Back Posture
Flat Back Posture occurs when the lower back loses its natural curve. This posture can lead to discomfort and pain. It affects how the spine aligns under gravity's force. Individuals with flat back posture often lean forward while standing or sitting.
This position may cause strain on muscles and ligaments.
Good posture is essential for health and wellbeing. Flat Back Posture can result in fatigue, decreased flexibility, and increased risk of injury. Improving this posture involves proper exercises that target spinal alignment.
Seeking professional help for posture correction ensures effective treatment options are available. Ergonomic support also plays a key role in maintaining an upright posture during daily activities.
Risks & Effects of Different Postures
Poor posture can lead to various health issues over time. Forward head and sway back postures may increase the risk of neck and back pain, while flat back posture can cause discomfort during movement.
Possible risks of Forward Head Posture
Forward Head Posture places strain on the neck and shoulders. It often leads to discomfort or pain in these areas. People may experience tension headaches due to this posture. Additionally, it can affect spinal alignment and overall body function.
This poor alignment increases the risk of musculoskeletal issues over time.
Health consequences arise from Forward Head Posture as well. Breathing can become shallow, reducing oxygen intake during physical activities. This issue affects dynamic posture when individuals move or exercise.
Maintaining good posture is crucial for health and wellbeing, making awareness of Forward Head Posture important for everyone.
Possible risks of Sway Back Posture
Sway back posture occurs when the pelvis tilts backward. This position can strain muscles and ligaments in the lower back. Over time, it may lead to chronic pain and discomfort. Sway back posture also affects balance and stability during movement.
Poor alignment influences your ability to perform functional movements effectively. People with this posture often face fatigue due to increased muscle workload.
Static posture plays a key role in how your body feels at rest, such as while sitting or standing. Misalignment from sway back can lead to health issues over time. It is essential to address these risks early on for better overall health and wellbeing.
Engaging in specific exercises helps improve posture and reduces risks of musculoskeletal problems related to sway back alignment.
Possible risks of Flat Back Posture
Flat Back Posture can lead to various health issues. This posture occurs when the natural curve of your lower back flattens, causing strain on the spine. Individuals with this posture often experience back pain and discomfort.
They may also feel tightness in their hamstrings and hips.
Reduced flexibility often accompanies Flat Back Posture. This limitation impacts movement during physical activities, such as walking or exercising. Over time, this poor alignment can increase the risk of musculoskeletal disorders.
Understanding its effects helps in promoting better posture practices for overall health and wellbeing.
How to Improve Posture
To improve your posture, practice simple exercises that strengthen your core and back muscles, and choose ergonomic furniture for better support. Explore more tips to enhance your posture effectively.
Tips for improving static posture
Good static posture plays a crucial role in your overall health. It involves maintaining proper alignment of your joints while sitting, standing, or lying down.
- Maintain an upright position while sitting. Sit with your back straight against the chair and keep your feet flat on the floor.
- Adjust your computer screen to eye level. Position the screen about an arm's length away and ensure it is at eye level to prevent forward head posture.
- Use ergonomic furniture for better support. Choose chairs and desks designed to promote good health and comfort during long hours of work or study.
- Keep your shoulders relaxed and aligned with your ears. Tension in the shoulders can negatively affect static posture.
- Strengthen core muscles through exercise. Strong core muscles provide stability that supports proper body alignment when sitting or standing still.
- Change positions frequently throughout the day. Avoid staying in one position for too long to reduce strain on joints and muscles.
- Practice mindfulness about body alignment during daily activities. Being aware of how you hold your body can help you maintain better static posture.
- Invest in lumbar support if necessary. A supportive cushion can help maintain the natural curve of your lower back when seated for extended periods.
- Perform stretches regularly for flexibility improvement. Stretching helps alleviate tension built up from poor static postures, particularly after long periods of inactivity.
- Seek professional help if needed for posture correction therapy or training sessions focused on improving both static and dynamic posture effectively.
Improving static posture positively impacts overall health by reducing risks associated with poor alignment, such as musculoskeletal issues.
Tips for improving dynamic posture
Dynamic posture plays a key role in maintaining health during movement. Improving this posture can prevent injuries and enhance performance.
- Focus on your body alignment when walking or running. Ensure that your head, shoulders, and hips form a straight line. This helps maintain good dynamic posture.
- Engage your core muscles actively while you move. Strong core support stabilizes your spine and encourages better alignment.
- Use proper footwear that supports your feet during physical activities. Good shoes improve stability and aid in achieving neutral posture throughout movement.
- Incorporate regular stretching breaks into your routine. Stretching helps maintain flexibility in muscles and joints, which supports dynamic posture.
- Practice exercises that promote balance, such as yoga or tai chi. These activities strengthen core muscles and enhance overall body control.
- Pay attention to your breathing while moving. Proper breathing techniques help you stay relaxed, which can improve movement quality.
- Adjust your workspace ergonomically when sitting for extended periods. A well-structured environment reduces strain on the body and promotes good sitting posture.
- Limit screen time to decrease slouching tendencies during prolonged use of devices. Frequent breaks can help reset your position and reduce forward head posture risks.
- Maintain awareness of how you carry objects while moving around. Keeping items close to your body prevents strain, supporting better dynamic posture during lifting tasks.
- Seek professional advice if you experience pain related to poor posture during movement activities. Consulting a specialist can provide personalized strategies for improvement.
Exercises for improving posture
Exercises can enhance posture and reduce health risks. Engaging in specific movements helps strengthen muscles that support good alignment.
- Wall Angels: Stand against a wall with your heels, back, and head touching it. Raise your arms to form a "W" position, then slide them up to a "Y." This exercise strengthens the upper back and improves shoulder mobility.
- Plank: Lie face down on the floor. Lift your body using your forearms and toes while keeping a straight line from head to heels. This core-strengthening exercise supports static posture by stabilizing the spine.
- Chest Opener Stretch: Stand tall and interlace your fingers behind your back. Straighten your arms and lift them gently upwards while opening your chest. This stretch counteracts slumping shoulders often caused by forward head posture.
- Bird-Dog: Start on all fours with hands under shoulders and knees under hips. Extend one arm forward while stretching the opposite leg back. Hold for a few seconds, then switch sides. This dynamic exercise promotes balance and stability.
- Bridge: Lie on your back with knees bent and feet flat on the floor. Raise your hips towards the ceiling while squeezing your glutes at the top of the motion. This strengthens the lower back and aids in overall body alignment.
- Seated Neck Stretch: Sit comfortably in a chair, keeping both feet flat on the ground. Tilt your head to one side, bringing your ear towards that shoulder until you feel a gentle stretch in the neck area. This helps alleviate tension from bad postures like forward head posture.
- Cat-Cow Stretch: Begin on all fours with hands under shoulders and knees under hips. Arch your back while looking up (Cow), then round it while tucking your chin (Cat). This flow improves flexibility in spinal alignment through dynamic movement.
- Hip Flexor Stretch: Stand tall or kneel down with one foot forward in a lunge position while keeping the other knee on the ground behind you. Push forwards gently to stretch hip flexors that tighten due to prolonged static postures from sitting.
- Shoulder Blade Squeeze: Sit or stand upright with arms at sides; squeeze shoulder blades together as if holding a pencil between them for five seconds before relaxing them down again - repeat several times for improved upper body posture control.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Adjust workstations for optimal alignment during activities like typing or using screens; ensure monitors are eye level, chairs provide proper lumbar support, encouraging healthy resting posture throughout daily tasks like standing or sitting.
Engaging regularly in these exercises fosters good posture habits over time, enhancing overall health outcomes associated with static and dynamic movement postures as well as promoting ergonomic posture at work or home environments.
The importance of ergonomic support
Ergonomic support plays a crucial role in maintaining good posture. It helps align the body correctly while sitting or standing, reducing strain on joints and muscles. A well-designed chair or desk encourages proper static posture during long hours of work.
Ergonomics also improves dynamic posture by providing stability and comfort as you move. This support decreases the risk of musculoskeletal issues that arise from poor positioning.
Investing in ergonomic tools benefits your health significantly. Good posture enhances overall wellbeing by promoting better circulation and reducing discomfort. People who pay attention to their environment experience fewer aches and pains.
With effective ergonomic solutions, individuals can improve both static and dynamic postures while enjoying daily activities more comfortably.
Seeking professional help for posture correction
Professional help can significantly improve posture correction. Trained specialists assess your body alignment and movement patterns. They focus on how joints align under gravity while standing or sitting.
This assessment helps identify static and dynamic posture issues. Good posture is essential for overall health and wellbeing.
Health experts may recommend tailored exercises to strengthen muscles and enhance stability. These exercises target specific postural weaknesses found in assessments. Supportive tools, like ergonomic chairs, can also aid in maintaining proper alignment.
Consulting with a professional ensures you receive personalized advice for effective posture improvement strategies.
FAQs
1. What are the types of postures?
There are two main types of postures: static and dynamic. Static posture is when you hold yourself in one position, like standing or sitting, while dynamic posture refers to how you carry yourself when moving.
2. How does good and bad posture affect health?
Good posture supports exercise physiology by aligning your body correctly for efficient movement. On the other hand, bad posture can lead to health problems such as back pain and muscle fatigue.
3. Can understanding my standing posture improve my health?
Yes, comprehending your standing posture - a form of static posture - can help identify any imbalances that may negatively impact your health over time.
4. Are there exercises designed to improve both static and dynamic postures?
Yes, specific exercises focus on improving both static and dynamic postures by strengthening key muscles involved in maintaining proper alignment during stillness or movement.